macaca源码分析-android-uiautomator
由于新手接触自动化来说,很多知识需要恶补,其中对于自动化脚本是如何通过指令发送到手机,感觉很是神奇,因此对于macaca中如何通过脚本操控手机这块进行了相关的研究,发现,在macaca中,操控安卓手机主要有两种方式:
1. 直接对底层adb指令进行封装,上层进行相关调用,比如截图啊、查询设备啊之类
2. 通过安卓自动化框架封装的Uiautomator进行相关封装
本文主要分析macaca中对于Uiautomator的封装的讨论
前提准备
1. macaca-adb
2. macaca-android
3. uiautomator-client
软件下载方式
可以通过两种方式获取:
1. 安装macaca-cli及android驱动,[可以参考macaca环境搭建](https://codetosurvive1.github.io/posts/macaca-environment.html),安装成功后会在对应的目录下生成node_moduels下,可以直接查看/usr/local/lib/node_modules/macaca-android驱动,该驱动依赖于macaca-adb以及uiautomator-client
2. 源码方式查看,直接从github下载源代码并安装相关依赖包
软件下载
这里直接使用上面的第二种方式,源码下载安装方式查看
1.下载源代码
mac:macaca mac$ git clone https://github.com/macacajs/macaca-android.git
Cloning into 'macaca-android'...
remote: Counting objects: 337, done.
remote: Compressing objects: 100% (35/35), done.
remote: Total 337 (delta 22), reused 0 (delta 0), pack-reused 302
Receiving objects: 100% (337/337), 54.47 KiB | 64.00 KiB/s, done.
Resolving deltas: 100% (222/222), done.
Checking connectivity... done.
2.安装依赖
mac:macaca mac$ cd macaca-android/
mac:macaca-android mac$ npm install
3.这里使用webstorm打开macaca-android工程
webstorm中工程截图如下
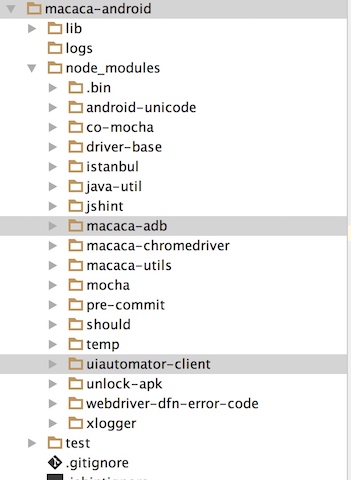
源码分析
macaca-android代码目录lib下核心代码为controllers.js和macaca-android.js
macaca-android.js中构造函数
class Android extends DriverBase {
constructor() {
super();
this.adb = null;
this.apkInfo = null;
this.args = null;
this.chromedriver = null;
this.chromeDriverPort = null;
this.proxy = null;
this.udid = null;
this.uiautomator = null;
this.isChrome = null;
this.isVirtual = true;
this.moveToPosition = null;
this.contexts = [];
}
}
启动设备
Android.prototype.startDevice = function *(caps) {
this.args = _.clone(caps);
this.isChrome = this.args.browserName && this.args.browserName.toLowerCase() === 'chrome';
yield JAVA.getVersion();
this.initReuse();
this.initAdb();
yield this.initDevice();
yield this.initUiautomator();//初始化UIautomator
yield this.getApkInfo();
yield this.unlock();
yield this.setIME();
yield this.launchApk();
yield this.waitActivityReady();
if (this.isChrome) {
yield this.getWebviews();
}
};
Android.prototype.initUiautomator = function *() {
this.uiautomator = new UIAutomator();
yield this.uiautomator.init(this.adb);
};
UIAutomator引入包uiautomator-client
const UIAutomator = require('uiautomator-client');
查看uiautomator-client包下lib下的uiautomator-client.js
UIAutomator的构造函数及init方法
function UIAutomator() {
this.adb = null;
this.socket = null;
this.socketPort = 6789;
this.queue = [];
}
UIAutomator.prototype.init = function *(adb) {
this.adb = adb;
const ANDROID_TMP_DIR = this.adb.getTmpDir();
try {
yield this.adb.rm(`${ANDROID_TMP_DIR}/${FILE_NAME}.jar`);
} catch (e) {
}
if (!_.isExistedFile(binPath)) {
logger.error(`uiautomator-bootstrap was not found in: ${binPath}, please check your Android ENV`);
return;
}
yield this.adb.push(binPath, ANDROID_TMP_DIR);
try {
yield this.adb.killProcess('uiautomator');
} catch (e) {
}
yield this.adb.forward(this.socketPort, this.socketPort);
yield this.initSocketServer();
yield this.initSocketClient();
};
从上面的构造函数及init方法中可以看出,默认构造了6789端口,然后调用init初始化方法中,首先删除了安卓手机临时目录’/data/local/tmp’中的uiautomator-bootstrap.jar包,然后上传jar包到临时目录下,并杀掉手机中的uiautomator进程,并将手机端口与电脑端口进行映射,最后初始化手机端的服务器及电脑端的客户端连接。
UIAutomator.prototype.initSocketServer = function() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
const ANDROID_TMP_DIR = this.adb.getTmpDir();
let args = `shell uiautomator runtest ${ANDROID_TMP_DIR}/${FILE_NAME}.jar -c ${CLASS_NAME} -e port ${this.socketPort} -e flag ${READY_FLAG}`.split(' ');
var proc = this.adb.spawn(args, {
path: process.cwd(),
env: process.env
});
proc.stderr.setEncoding('utf8');
proc.stdout.setEncoding('utf8');
proc.stdout.on('data', data => {
if (!!~data.indexOf(READY_FLAG)) {
logger.info('socket server ready');
resolve();
} else {
console.log(data);
}
});
proc.stderr.on('data', data => {
console.log(data);
});
});
};
初始化手机服务端方法中,可以看出是直接调用通过adb shell调用手机中的uiautomator执行uiautomator的测试集adb shell uiautomator runtest ${ANDROID_TMP_DIR}/${FILE_NAME}.jar -c ${CLASS_NAME} -e port ${this.socketPort} -e flag ${READY_FLAG},这里的${ANDROID_TMP_DIR}/${FILE_NAME}.jar指的是/data/local/tmp/uiautomator-bootstrap.jar,-c指定要运行的测试类,即为com.android.uiautomator.client.Initialize,-e指定参数,这里指定了两个参数,一个是port,一个是flag
UIAutomator.prototype.initSocketClient = function() {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
this.socket = net.connect(this.socketPort, () => {
logger.info('socket client ready');
resolve();
});
var tempData = '';
this.socket.setEncoding('utf8');
this.socket.on('data', data => {
try {
let res = JSON.parse(tempData + data);
tempData = '';
let success = res.success;
if (success) {
this.queue.shift().resolve(res.data);
} else {
this.queue.shift().reject();
}
} catch (e) {
tempData += data;
}
});
this.socket.on('end', () => {
logger.warn('connect lost');
});
});
};
电脑客户端连接比较简单,直接连接上服务端,并注册监听事件。
UIAutomator.prototype.send = function *(cmd) {
var defer = new _.Defer();
defer.promise.then(data => {
});
this.queue.push(defer);
this.socket.write(`${JSON.stringify(cmd)}\n`);
return yield defer.promise;
};
这是另外的一个发送的方法send,直接将指令发送到服务端,该方法的调用在macaca-android.js中,这里很简单直接调用并返回响应码
Android.prototype.send = function *(data) {
try {
var result = yield this.uiautomator.send(data);
} catch (err) {
logger.debug(`UnknownError from uiautomator ${err}`);
throw new errors.UnknownError();
}
var statusCode = result.status;
if (statusCode === 0) {
return result.value;
} else {
var errName = getErrorByCode(statusCode);
if (!errName) {
throw new errors.UnknownError();
}
throw new errors[errName](result.value);
}
};
手机端uiautomator源码导入
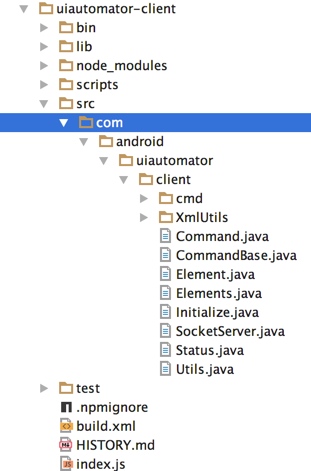
从这里的目录可以看出macaca中对于uiautomator的java源代码封装,下面使用idea进行相关源码导入或者直接通过github下载并添加lib下的jar包
1.建立普通java工程
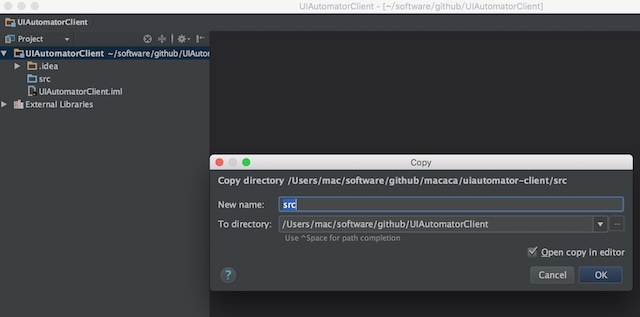
2.uiautomator-client目录下的src拷贝到创建的java工程中
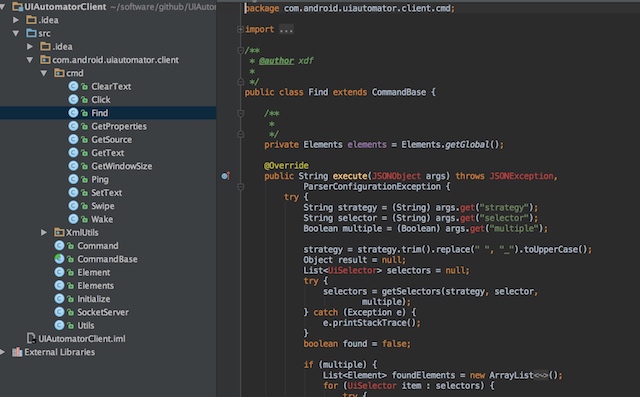
3.添加uiatuomator,android,及fastjson的jar包,添加成功后,代码中不报错
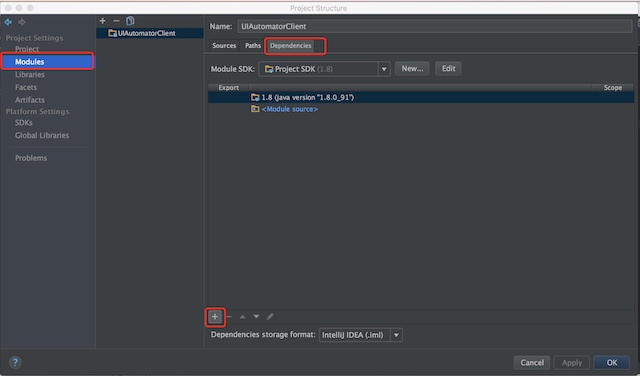
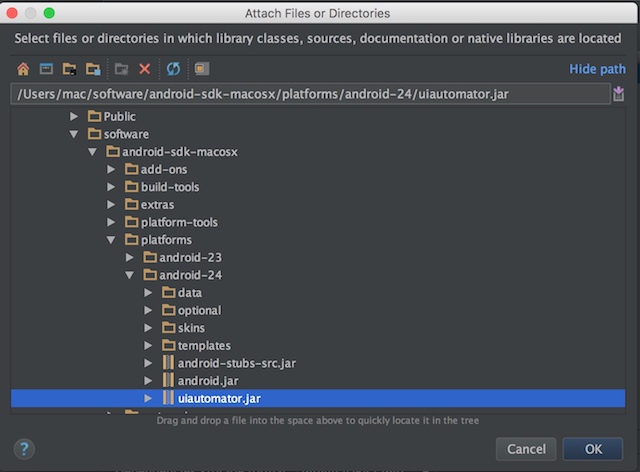
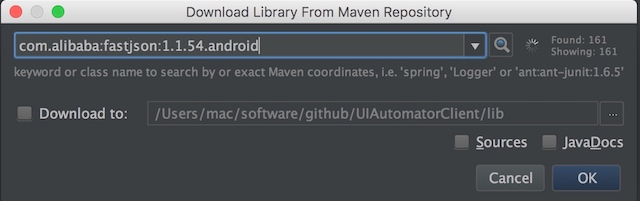
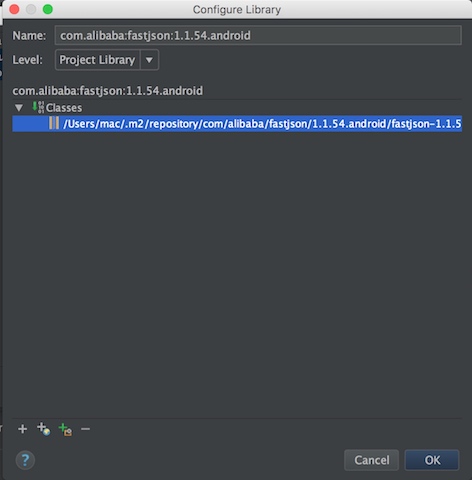
手机端uiautomator源码分析
1.直接查看上面js中指定的com.android.uiautomator.client.Initialize源码
public class Initialize extends UiAutomatorTestCase {
/**
* @throws IOException
* @throws JSONException
* @throws ParserConfigurationException
*/
public void testStartServer() throws IOException, JSONException,
ParserConfigurationException {
Utils.output("uiautomator start socket server.");
int port = Integer.parseInt(getParams().getString("port"));
String readyFlag = getParams().getString("flag");
SocketServer server = new SocketServer(port);
server.listen(readyFlag);
}
}
可以看出,该类直接继承自uiautomator框架中的UiAutomatorTestCase,该方法直接获取传递进来的参数port和flag,并传递给SocketServer类
2.SocketServer类是简单的java tcp服务端实现类
public class SocketServer {
private ServerSocket server;
public SocketServer(int port) throws IOException {
setServer(new ServerSocket(port));
}
/**
* @param readyFlag
* @throws JSONException
* @throws ParserConfigurationException
*/
public void listen(String readyFlag) throws JSONException,
ParserConfigurationException {
Utils.output(readyFlag);
try {
Socket client = server.accept();
BufferedReader input = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
client.getInputStream(), "UTF-8"));
BufferedWriter output = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(
client.getOutputStream(), "UTF-8"));
StringBuilder swap = new StringBuilder();
while (true) {
swap.setLength(0);
int chunk;
while ((chunk = input.read()) != -1 && input.ready()) {
swap.append((char) chunk);
}
String str = swap.toString();
Utils.output("recive: " + str);
String res = Command.handleInput(str);
Utils.output("return: " + res);
output.write(res);
output.flush();
}
} catch (final IOException e) {
}
}
/**
* @return res
*/
public ServerSocket getServer() {
return server;
}
/**
* @param server
*/
public void setServer(ServerSocket server) {
this.server = server;
}
}
该类的核心代码在listen方法,该方法即为死循环,不停的接受发送过来的指令,然后处理执行Command.handleInput,并将处理的结果返回
3.Command.handleInput处理接受到的指令并解析,并根据命令将命令参数传递给不同的实现类
public class Command {
/**
*
*/
private static HashMap<String, CommandBase> map = new HashMap<String, CommandBase>();
static {
getMap().put("ping", new Ping());
getMap().put("wake", new Wake());
getMap().put("find", new Find());
getMap().put("setText", new SetText());
getMap().put("getText", new GetText());
getMap().put("click", new Click());
getMap().put("clearText", new ClearText());
getMap().put("swipe", new Swipe());
getMap().put("getWindowSize", new GetWindowSize());
getMap().put("getProperties", new GetProperties());
getMap().put("getSource", new GetSource());
}
/**
* @param input
* @return res
* @throws JSONException
* @throws ParserConfigurationException
*/
static String handleInput(String input) throws JSONException,
ParserConfigurationException {
JSONObject json = Utils.parseJSON(input);
String cmd = (String) json.get("cmd");
JSONObject args = (JSONObject) json.get("args");
return getMap().get(cmd).execute(args);
}
/**
* @return res
*/
public static HashMap<String, CommandBase> getMap() {
return map;
}
/**
* @param map
*/
public static void setMap(HashMap<String, CommandBase> map) {
Command.map = map;
}
}
其中的handleInput即接受指令,然后从指令中获取命令和命令参数,并调用getMap().get(cmd).execute(args),而getMap()中的map的初始化在static域中
| 命令 | 处理类 | 作用 |
| ping | Ping() | 测试连通 |
| wake | Wake() | 模拟按电源键 |
| find | Find() | 查找页面元素 |
| setText | SetText() | 设置文本内容 |
| getText | GetText() | 获取文本内容 |
| cick | Click() | 点击元素 |
| clearText | ClearText() | 清空元素内容 |
| swipe | Swipe() | 滑动 |
| getWindowSize | GetWindowSize() | 获取手机长宽 |
| getProperties | GetProperties() | 获取手机属性 |
| getSource | GetSource() | 获取当前画面的dump的xml文件 |
4.各个处理类分析
4.1 Ping代码分析,该方法直接返回成功标志,实际上没有具体的业务含义,可能只是为了测试手机服务端启动的成功与否
public class Ping extends CommandBase {
@Override
public String execute(JSONObject args) throws JSONException {
try {
return success((Object) "it works!");
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return failed("UnknownError");
}
}
}
4.2 Wake 模拟电源按键,核心调用的UiDevice中的wakeUp方法
public class Wake extends CommandBase {
@Override
public String execute(JSONObject args) throws JSONException {
try {
UiDevice.getInstance().wakeUp();
return success((Object) true);
} catch (final RemoteException e) {
Utils.output(e.toString());
}
return failed("UnknownError");
}
}
4.3 SetText 设置文本内容,该处理类也是同样根据传递进来的ElementId获取到macaca封装的Element元素后,调用setText方法,核心也是调用的UiObject中的setText方法
public class SetText extends CommandBase {
@Override
public String execute(JSONObject args) throws JSONException {
try {
String elementId = (String) args.get("elementId");
String text = (String) args.get("text");
Element element = Elements.getGlobal().getElement(elementId);
boolean needPressEnter = false;
if (text.endsWith("\\n")) {
needPressEnter = true;
text = text.replace("\\n", "");
}
Charset UTF7 = Charset.forName("UTF-7");
Charset ASCII = Charset.forName("US-ASCII");
byte[] encoded = text.getBytes(UTF7);
String str = new String(encoded, ASCII);
boolean result = element.setText(str);
if (needPressEnter) {
final UiDevice d = UiDevice.getInstance();
d.pressEnter();
}
return success(result);
} catch (final UiObjectNotFoundException e) {
return failed("NoSuchElement");
} catch (final Exception e) {
return failed("UnknownError");
}
}
}
4.4 GetText 获取文本内容,该处理类也是同样根据传递进来的ElementId获取到macaca封装的Element元素后,调用getText方法,核心也是调用的UiObject中的getText方法
public class GetText extends CommandBase {
@Override
public String execute(JSONObject args) throws JSONException {
try {
String elementId = (String) args.get("elementId");
Element element = Elements.getGlobal().getElement(elementId);
return success(element.getText());
} catch (final Exception e) {
return failed("UnknownError");
}
}
}
4.5 Click 点击操作 该处理类也是同样根据传递进来的ElementId获取到macaca封装的Element元素后,调用click方法,核心也是调用的UiObject中的click方法
public class Click extends CommandBase {
@Override
public String execute(JSONObject args) throws JSONException {
try {
String elementId = (String) args.get("elementId");
Element el = Elements.getGlobal().getElement(elementId);
el.click();
return success(true);
} catch (final UiObjectNotFoundException e) {
return failed("NoSuchElement");
} catch (final Exception e) {
return failed("UnknownError");
}
}
}
4.6 ClearText 清空文本 该操作类通过参数中获取的元素id获取到元素后,直接调用Element元素的clearText方法,而Element元素是macaca自己封装的Uiautomator中的UIObject类中的clearTextField方法
public class ClearText extends CommandBase {
@Override
public String execute(JSONObject args) throws JSONException {
try {
String elementId = (String) args.get("elementId");
Element el = Elements.getGlobal().getElement(elementId);
el.clearText();
return success(true);
} catch (final UiObjectNotFoundException e) {
return failed("NoSuchElement");
} catch (final Exception e) {
return failed("UnknownError");
}
}
}
public UiObject element;
/**
* @throws UiObjectNotFoundException
*/
public void clearText() throws UiObjectNotFoundException {
element.clearTextField();
}
4.7 Swipe 滑动 该处理类直接根据参数获取(开始位置坐标,结束位置坐标)+持续时间,然后直接调用UiDevice中的swipe滑动方法实现
public class Swipe extends CommandBase {
@Override
public String execute(JSONObject args) throws JSONException {
try {
Integer startX = (Integer) args.get("startX");
Integer startY = (Integer) args.get("startY");
Integer endX = (Integer) args.get("endX");
Integer endY = (Integer) args.get("endY");
Integer duration = (Integer) args.get("duration");
boolean result = UiDevice.getInstance().swipe(startX, startY, endX, endY, duration);
return success(result);
} catch (final Exception e) {
return failed("UnknownError");
}
}
}
4.8 GetWindowSize 获取手机长宽 直接调用UiDevice获取长度和宽度返回
public class GetWindowSize extends CommandBase {
@Override
public String execute(JSONObject args) throws JSONException {
try {
Integer width = UiDevice.getInstance().getDisplayWidth();
Integer height = UiDevice.getInstance().getDisplayHeight();
JSONObject size = new JSONObject();
size.put("width", width);
size.put("height", height);
return success(size.toString());
} catch(JSONException e) {
return failed("UnknownError");
}
}
}
4.9 GetProperties 获取手机属性 包括元素长度、宽度、中心坐标、左上位置坐标、面积
public class GetProperties extends CommandBase {
@Override
public String execute(JSONObject args) throws JSONException {
try {
String elementId = (String) args.get("elementId");
Element el = Elements.getGlobal().getElement(elementId);
final Rect rect = el.element.getBounds();
JSONObject size = new JSONObject();
size.put("width", rect.width());
size.put("height", rect.height());
size.put("centerX", rect.centerX());
size.put("centerY", rect.centerY());
JSONObject origin = new JSONObject();
origin.put("x", rect.left);
origin.put("y", rect.top);
JSONObject props = new JSONObject();
props.put("origin", origin);
props.put("size", size);
return success(props.toString());
} catch (final UiObjectNotFoundException e) {
return failed("NoSuchElement");
} catch (final Exception e) {
return failed("UnknownError");
}
}
}
4.10 GetSource 获取当前画面的dump的xml文件 直接调用UiDevice中的dump方法生成macaca-dump.xml文件,然后在js中通过adb命令pull拉取到电脑本地文件系统中
public class GetSource extends CommandBase {
private static final String dumpFileName = "macaca-dump.xml";
@Override
public String execute(JSONObject args) throws JSONException {
try {
final File dump = new File(new File(Environment.getDataDirectory(),
"local/tmp"), dumpFileName);
dump.mkdirs();
if (dump.exists()) {
dump.delete();
}
UiDevice.getInstance().dumpWindowHierarchy(dumpFileName);
return success(true);
} catch (final Exception e) {
return failed("UnknownError");
}
}
}
4.11 Find 查找页面元素 首先传递参数需要三个
策略:即为通过什么来获取元素,这里有class_Name、name、id、xpath
值:即策略所对应的取值
是否支持多个查询:是否支持多个查询或者找到匹配元素即返回
public class Find extends CommandBase {
private Elements elements = Elements.getGlobal();
@Override
public String execute(JSONObject args) throws JSONException,
ParserConfigurationException {
try {
String strategy = (String) args.get("strategy");
String selector = (String) args.get("selector");
Boolean multiple = (Boolean) args.get("multiple");
strategy = strategy.trim().replace(" ", "_").toUpperCase();
Object result = null;
List<UiSelector> selectors = null;
try {
selectors = getSelectors(strategy, selector,
multiple);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
boolean found = false;
if (multiple) {
List<Element> foundElements = new ArrayList<Element>();
for (UiSelector item : selectors) {
try {
final List<Element> elementsFromSelector = getElements(item);
foundElements.addAll(elementsFromSelector);
} catch (final UiObjectNotFoundException ignored) {
}
}
found = foundElements.size() > 0;
result = elementsToJSONArray(foundElements);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < selectors.size() && !found; i++) {
try {
result = getElement(selectors.get(i));
found = result != null;
} catch (Exception ignored) {
Utils.output("ignored selector");
}
}
}
if (!found) {
return failed("ElementNotFound");
}
return success((Object) result);
} catch (JSONException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return failed("UnknownError");
}
}
/**
* @param strategy
* @param text
* @param multiple
* @return res
* @throws ParserConfigurationException
*/
private List<UiSelector> getSelectors(String strategy, String text,
boolean multiple) throws Exception {
final List<UiSelector> list = new ArrayList<UiSelector>();
UiSelector selectors = new UiSelector();
if (strategy.equals("CLASS_NAME")) {
selectors = selectors.className(text);
if (!multiple) {
selectors = selectors.instance(0);
}
list.add(selectors);
} else if (strategy.equals("NAME")) {
selectors = new UiSelector().description(text);
if (!multiple) {
selectors = selectors.instance(0);
}
list.add(selectors);
selectors = new UiSelector().text(text);
if (!multiple) {
selectors = selectors.instance(0);
}
list.add(selectors);
} else if (strategy.equals("ID")) {
selectors = selectors.resourceId(text);
if (!multiple) {
selectors = selectors.instance(0);
}
list.add(selectors);
} else if(strategy.equals("XPATH")) {
final ArrayList<UiSelector> pairs = XmlUtils.getSelectors(text);
if (!multiple) {
if (pairs.size() == 0) {
throw new Exception("Could not find an element using given xpath expression.");
}
list.add(pairs.get(0));
} else {
for (final UiSelector pair : pairs) {
list.add(pair);
}
}
}
return list;
}
/**
* @param sel
* @return res
* @throws JSONException
* @throws Exception
*/
private JSONObject getElement(final UiSelector sel) throws JSONException,
Exception {
final JSONObject res = new JSONObject();
final Element element = getElements().getElement(sel);
return res.put("ELEMENT", element.getId());
}
/**
* @param sel
* @return res
* @throws UiObjectNotFoundException
*/
private ArrayList<Element> getElements(final UiSelector sel)
throws UiObjectNotFoundException {
return elements.getElements(sel);
}
/**
* @param elems
* @return res
* @throws JSONException
*/
private JSONArray elementsToJSONArray(final List<Element> elems)
throws JSONException {
JSONArray resArray = new JSONArray();
for (Element element : elems) {
resArray.put(new JSONObject().put("ELEMENT", element.getId()));
}
return resArray;
}
/**
* @return res
*/
public Elements getElements() {
return elements;
}
/**
* @param elements
*/
public void setElements(Elements elements) {
this.elements = elements;
}
}
疑问
既然macaca封装的时候通过两种方式进行封装,adb命令和uiautomator,那么何时使用adb?何时使用Uiautomator呢?带着疑问向macaca团队提出issue,相关疑问解答参考连接macaca-android驱动封装规则
原创文章,转载请注明出处!
本文链接:https://codetosurvive1.github.io/posts/macaca-source-analyze-android-uiautomator.html